In today’s digital age, where personal information is constantly being collected, stored, and transmitted, ensuring data privacy has become more critical than ever. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats and data breaches, individuals and organizations must take proactive steps to safeguard sensitive data from unauthorized access and misuse. In this comprehensive guide, Amqid.info will explore 12 effective ways to protect data privacy.
Effective Ways to Protect Data Privacy
1. Use Strong Passwords:
One of the simplest yet most effective ways to protect data privacy is by using strong passwords. Passwords act as the first line of defense against unauthorized access to accounts and sensitive information. It’s essential to create unique, complex passwords for each account, incorporating a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid using easily guessable passwords like “password” or “123456,” and consider using a reputable password manager to securely store and manage passwords.
2. Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA):
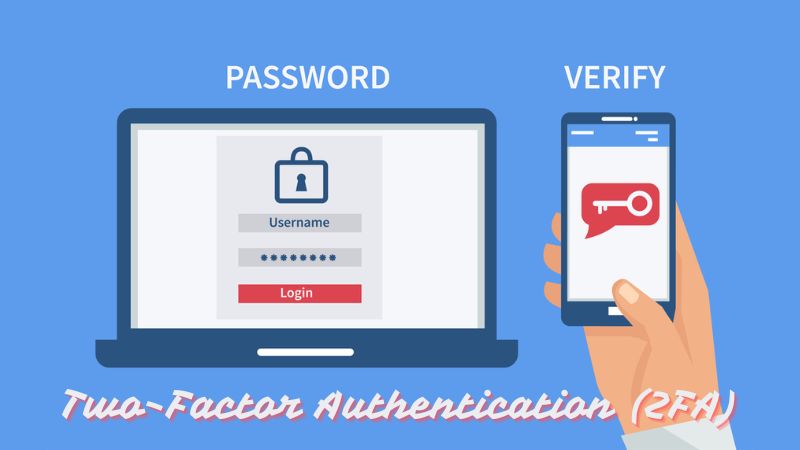
In addition to using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security to your accounts. 2FA requires users to provide a second form of identification, such as a code sent to their mobile device, after entering their password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if passwords are compromised. Many online services and platforms offer 2FA options that can be easily enabled in account settings.
3. Encrypt Data:
Encryption is a powerful tool for protecting data privacy both at rest and in transit. By encrypting sensitive data, it becomes unreadable to anyone without the appropriate decryption key. Utilize robust encryption algorithms to encrypt data stored on devices, servers, or in the cloud, as well as data transmitted over networks. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains secure and protected from unauthorized access.
4. Regularly Update Software and Systems:
Keeping software, operating systems, and applications up to date is crucial for maintaining data privacy and security. Software updates often include patches and fixes for known vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cyber attackers. By regularly updating your systems, you can stay ahead of potential threats and minimize the risk of data breaches or security incidents.

5. Limit Data Collection and Retention:
To protect data privacy, it’s essential to minimize the collection and retention of personal information. Only collect the data that is necessary for your operations and avoid gathering excessive or irrelevant information. Additionally, establish data retention policies to regularly review and delete outdated or unnecessary data. By limiting the amount of data you collect and retain, you can reduce the risk of data exposure and misuse.
6. Implement Access Controls:
Implementing access controls is crucial for ensuring that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data. Utilize role-based access controls (RBAC) to assign permissions based on users’ roles and responsibilities within the organization. This ensures that employees only have access to the data they need to perform their job functions and helps prevent unauthorized access or data breaches.
7. Train Employees:
Employees are often the weakest link in data privacy and security. Providing comprehensive training on data privacy best practices is essential for creating a culture of security within the organization. Educate employees about the importance of protecting sensitive information, recognizing phishing attempts, and securely handling data. Regular training sessions and awareness campaigns can help employees stay vigilant and proactive in protecting data privacy.
8. Secure Network Infrastructure:

Securing your network infrastructure is paramount for protecting data privacy. Implement firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and other security measures to monitor and control network traffic. Use encryption protocols such as SSL/TLS to secure data transmitted over networks, particularly in public Wi-Fi or untrusted environments. By securing your network infrastructure, you can prevent unauthorized access and mitigate the risk of data breaches.
9. Monitor and Audit:
Regular monitoring and auditing of network activities and access to data are essential for detecting and responding to potential security threats. Implement security monitoring tools and protocols to track user activity, detect anomalies, and identify potential security incidents. Conduct regular security audits to assess the effectiveness of security controls and identify any vulnerabilities or compliance issues that need to be addressed.
10. Privacy Policies and Consent:
Clearly communicating your organization’s privacy policies to customers and obtaining their consent before collecting or processing their personal data is crucial for maintaining data privacy compliance. Ensure that privacy policies are easily accessible and provide clear information about how personal data is collected, used, and protected. Obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting any sensitive information, and respect their preferences regarding data processing and sharing.
11. Secure Physical Storage:
In addition to securing digital data, it’s essential to secure physical storage of sensitive information. If you store physical copies of data, ensure that they are kept in secure locations with restricted access. Implement measures such as locked cabinets or secure shredding services to prevent unauthorized access or disposal of sensitive documents. By securing physical storage, you can protect data privacy both online and offline.
12. Backup Data:
Regularly backing up your data is essential for protecting against data loss due to hardware failure, cyber attacks, or other unforeseen events. Ensure that backups are securely stored and encrypted to prevent unauthorized access. Implement a comprehensive backup strategy that includes regular backups, offsite storage, and testing of backup systems to ensure data integrity and availability.
Sum Up
In conclusion, protecting data privacy is a multifaceted endeavor that requires a combination of technical controls, organizational policies, and employee awareness. By implementing the 12 effective ways to protect data privacy in this guide, individuals and organizations can enhance data privacy protection and mitigate the risk of data breaches and privacy violations. By prioritizing data privacy, we can build trust with customers, partners, and stakeholders while safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access and misuse.
